Mechanics Spotlights
This page is a collection of every spotlight or progress that highlights the development of the omnibase in the Mechanical design area.
2025-06-29
Started a proof of concept CAD:
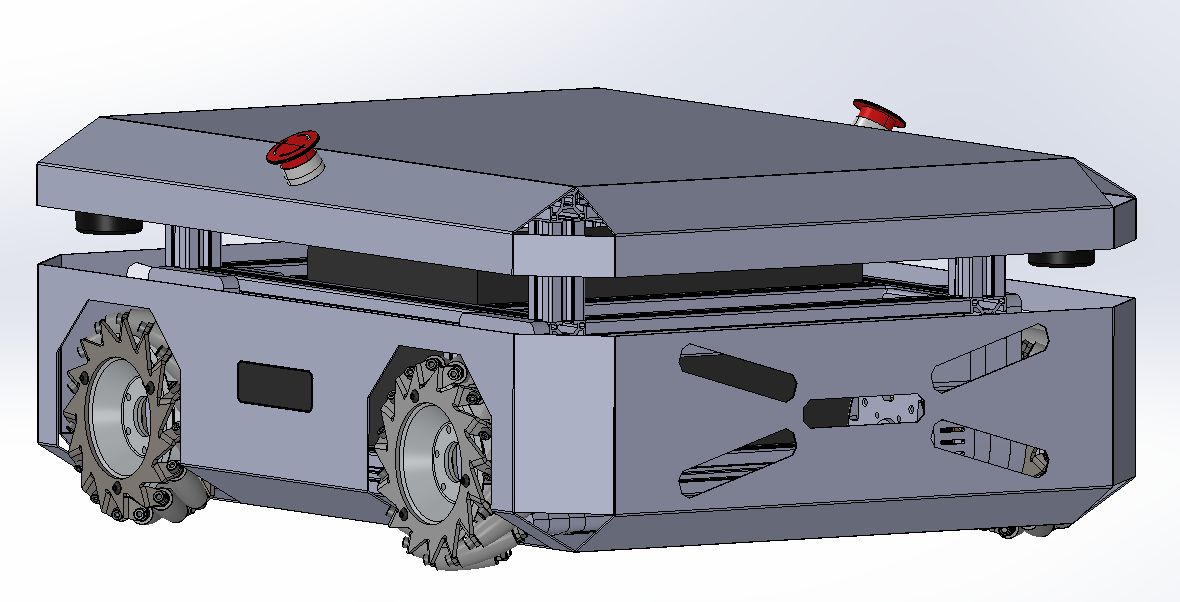
2025-06-19
A session was held to discuss which type of wheel to use, omnidirectional or mecanum, the insights found are summarized in the following table of advantages for each wheel type:
| Mecanum Wheels | Omni Wheels |
|---|---|
| Less vibration and greater stability | Smaller footprint |
| Easy chassis body fabrication because the wheels are mounted in line [1] | Navigation with ease in cramped spaces [2] |
| Greater pushing force in every direction, good for heavy load carrying applications [3] | Greater maximum velocity in every direction [3] |
| Possible place to buy them | Possible place to buy them |
From the research we concluded that the wheel choice does not have many differences from one to another, compared to what we initially thought, in fact most sources highlight more the programming differences than the mechanical ones.
Due to its greater performance on heavy load applications, and its efficieny on space usage as explained on figure 1 the selected wheel types was mecanum.
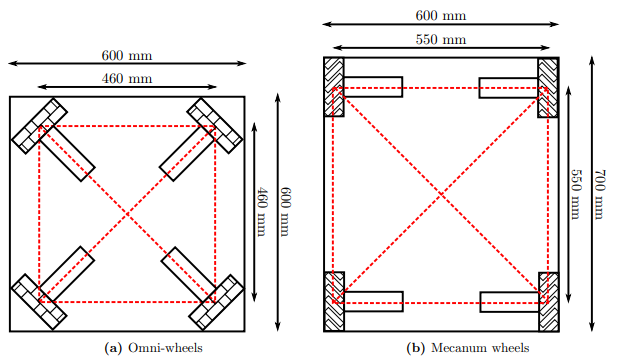
Figure 1: Space efficiency comparison between omni-wheels and mecanum wheels, image from [4]
References:
[1] K. Kanjanawanishkul, “Omnidirectional wheeled mobile robots: wheel types and practical applications,” International Journal of Advanced Mechatronic Systems, vol. 6, no. 6, p. 289, Jan. 2015, doi: 10.1504/ijamechs.2015.074788.
[2] Kang, “Tidyboy-OPL: RoboCup@Home Open Platform League Team Description Paper,” RoboCup, p. RoboCup @Home Qualification Material 2024, 2024, [Online]. Available: https://athome.robocup.org/wp-content/uploads/OPL-Tidyboy-OPL-TDP.pdf
[3] Mo. Massoud, Mostafa & Abdellatif Hamed IBRAHIM, Ahmed & Atia, Mostafa. (2021). Mechatronic Design and Path planning optimization for an Omni wheeled mobile robot for indoor applications. 90-98. 10.1109/ICCTA54562.2021.9916626.
[4] Lunenburg, J. J. M. (2015). Context-aware design and motion planning for autonomous service robots. [Phd Thesis 1 (Research TU/e / Graduation TU/e), Mechanical Engineering]. Technische Universiteit Eindhoven.